Reaction Vessel: Definition, Types, and Applications


Reaction Vessel: Definition, Types, and Applications
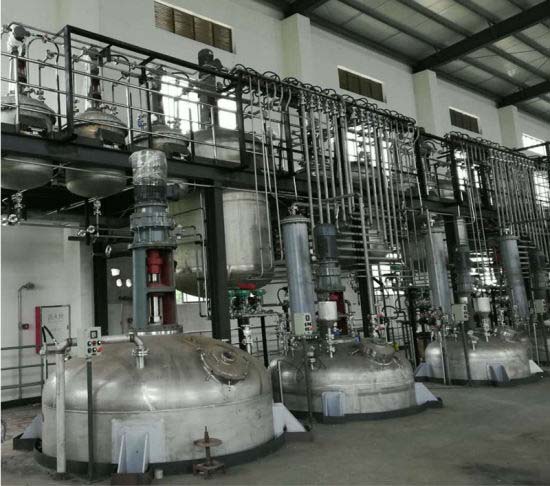
A reaction vessel is an industrial container or apparatus used for carrying out chemical reactions under controlled conditions. These vessels are essential in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, food processing, and biotechnology, where precise control over temperature, pressure, and mixing is required to drive specific chemical processes.
Key Features and Design of Reaction Vessel
Material Construction: Reaction vessels are typically made from materials that can withstand harsh chemical reactions, high temperatures, and pressures. Common materials include stainless steel, glass, and alloys, which offer resistance to corrosion and provide the necessary durability for different processes.
Size and Shape: The size and shape of a reaction vessel depend on the nature and scale of the reaction. Small-scale lab reactors may be designed as flasks or beakers, while large-scale industrial reactors could range from several liters to thousands of liters.
Temperature Control: Temperature is a critical factor in most chemical reactions. Reaction vessel are often equipped with heating and cooling systems, such as jackets, coils, or electrical heating elements, to regulate the reaction temperature and maintain optimal reaction conditions.
Pressure Control: Some reactions require elevated pressures to proceed at a desirable rate. Reaction vessel designed for high-pressure operations are built to handle internal pressures safely, with features like pressure relief valves, manometers, and burst discs.
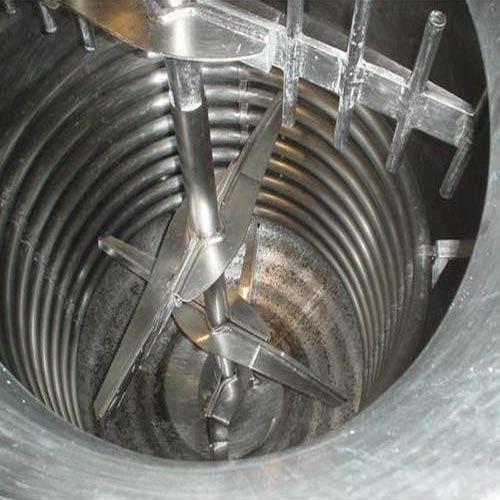
Agitation: In many reactions, efficient mixing is necessary to ensure proper contact between reactants. Stirring or agitation is commonly achieved using mechanical agitators, magnetic stirrers, or impellers that ensure homogeneous mixing within the vessel.
Sealing and Safety: Since many reactions produce hazardous by-products or require high temperatures and pressures, reaction vessels are often sealed to prevent leaks. They may also include safety features like pressure sensors, emergency venting systems, and fail-safe shutdown mechanisms.
Types of Reaction Vessels
Batch Reactors: These are used for reactions where all reactants are loaded into the vessel at the beginning of the process. The reaction occurs over a period of time, and the product is extracted once the reaction is complete. Batch reactors are ideal for small to medium-scale productions.
Continuous Reactors: Unlike batch reactors, continuous reactors maintain a constant flow of reactants into and out of the vessel. This type of reactor is used for large-scale, high-volume production processes where a continuous supply of product is needed.
Semi-batch Reactors: These reactors combine the features of batch and continuous systems. Some reactants are continuously fed into the vessel, while others are added intermittently. This type is useful for reactions that require precise control over reactant concentrations.
Fixed-bed Reactors: Used for catalytic reactions, fixed-bed reactors have a stationary bed of catalyst material through which the reactants flow. These reactors are typically used in petrochemical processes.
Fluidized-bed Reactors: These reactors use a fluidized state where solid particles, usually catalysts, are suspended by the flow of gas or liquid. This design enhances the contact between the reactants and the catalyst, improving the reaction efficiency.
Stirred Tank Reactors (STR): Stirred tank reactors are a common type of batch or continuous reactor that uses a mechanical stirring mechanism to ensure uniform mixing of the reactants. These are widely used in pharmaceutical, biochemical, and chemical engineering applications.
Applications of Reaction Vessels
Pharmaceutical Industry: In pharmaceutical manufacturing, reaction vessels are crucial for synthesizing compounds, active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), and intermediates. Precise control over the reaction environment is necessary to ensure product quality and consistency.
Petrochemical Industry: In the petrochemical sector, reaction vessels are used in refining processes, such as cracking, distillation, and catalytic reactions, to convert crude oil into valuable chemicals and fuels.
Food and Beverage: Reaction vessels are used in food processing for fermentation, pasteurization, and other chemical processes. They help ensure food safety and consistency in flavor and texture.
Environmental Engineering: Reaction vessels are involved in wastewater treatment and other environmental processes, such as bioreactors used for the degradation of pollutants or production of bio fuels.
Research and Development: In R&D, reaction vessels of various sizes (from laboratory scale to pilot scale) are used to explore new chemical processes, test reaction conditions, and develop new materials or products.